There are
few system requirements that must be met before you can install ESXi 6.0 server:
- Make sure the server hardware that you are going to install ESXi server on is supported by VMware vSphere. You can check that using VMware Compatibility Guide.
- The physical server must have 64-bit processors with at least two CPU cores.
- The physical server must have minimum of 4GB of RAM. You need at least 8GB memory to install a virtual machine after ESXi server is installed.
- The NX/XD bit must be enabled in the BIOS. Intel-VT for Intel processors and AMD-V for AMD processors.
- The physical server must have one or more Gigabit Ethernet adapter.
- Compatible disk storage.
- Make sure the server hardware that you are going to install ESXi server on is supported by VMware vSphere. You can check that using VMware Compatibility Guide.
- The physical server must have 64-bit processors with at least two CPU cores.
- The physical server must have minimum of 4GB of RAM. You need at least 8GB memory to install a virtual machine after ESXi server is installed.
- The NX/XD bit must be enabled in the BIOS. Intel-VT for Intel processors and AMD-V for AMD processors.
- The physical server must have one or more Gigabit Ethernet adapter.
- Compatible disk storage.
Install and Configure VMware ESXi 6.0
There are
different ways to install ESXi server. You can use interactive installation (CD/DVD, USB drive, and PXE
boot), scripts or auto deploy. Here, I will use
interactive method using CD/DVD media to install ESXi server. You can download installation ISO image from VMware. Let’s begin the
installation. First, make sure the server is configured to boot from CD/DVD.
Insert CD/DVD in to the DVD-ROM or map ISO image to virtual CD/DVD drive and
boot the server from ISO image.

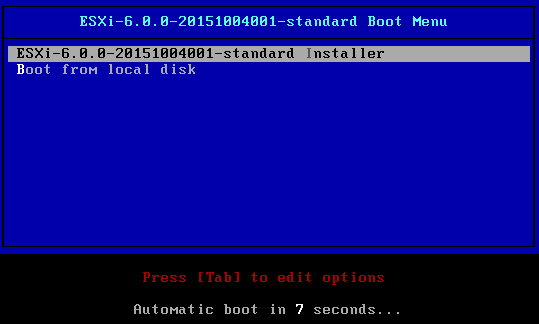
Once you
start the server with ESXi installation media, you will be presented with ESXi
standard boot menu as shown above. Choose ESXi standard installer to start the
ESXi installer. Press [Tab] to toggle the selection and press [Enter] to choose
the selection. As you can see above, you also have option to booth from local
disk.
Welcome
screen appears as shown above. Press [Enter] to begin the installation of ESXi
server.
Press F11
to accept the license agreement.
Choose the
storage and press [Enter] to continue. As you can see above the disk type is
VMware Virtual S, this is because I am installing ESXi server on a VMware
Workstation virtual machine. You can press F1 to see more details about the
disk. If you are installing ESXi server on a local SAS storage, it will be
listed as remote devices.
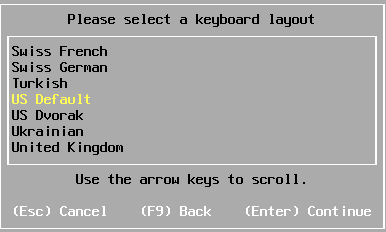
Choose the
keyboard layout. Press [Enter] to continue.
Enter the
password for root user account. The password must be at least 7 characters
long. Press [Enter] to continue.

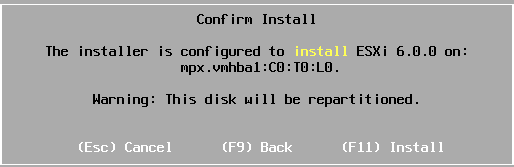
To confirm
the installation press F11.

The
installation now begins.

Press
[Enter] to reboot and complete the installation.
After the
reboot, you can see the Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) above. You can see
the ESXi build number, memory and processor information and IP address. As you
can see above by default, ESXi is set to receive IP from DHCP server. You can
press F2 to login to DCUI to change IP address, DNS, hostname and other
information.